Canada’s Record Low Fertility Rates in 2022
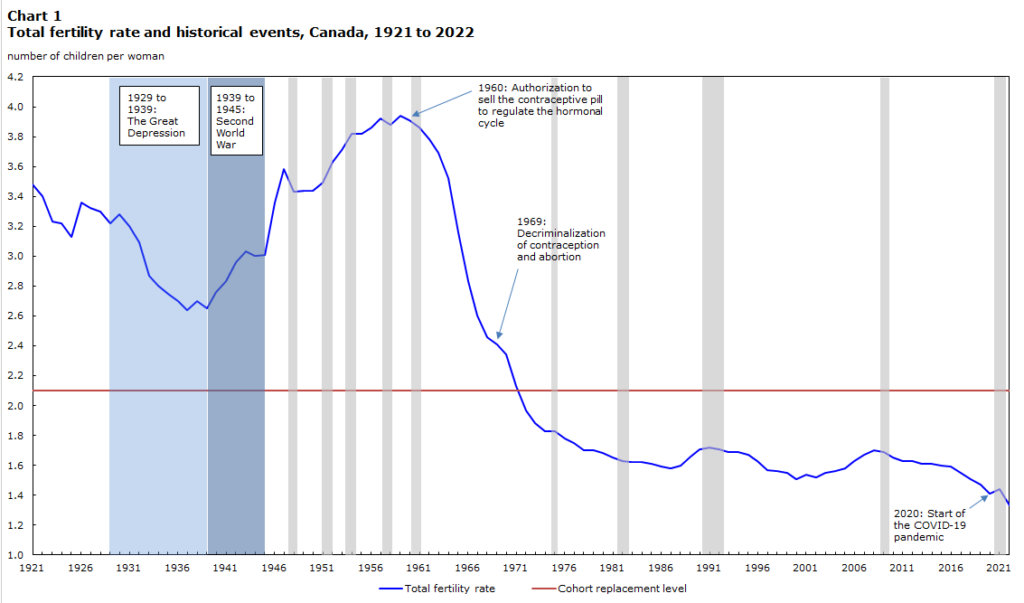
Canada recorded its lowest fertility rate ever recorded by Statistics Canada, which started tracking this over a century ago. Canada’s fertility rate fell to 1.33 per woman in 2022, which is far below replacement levels of 2.1. The fertility rate dropped from its level of 1.43 in 2021 and continues a downward trend that started in 2009. The average age of mothers when their kids were born was 31.6 years old in Canada and 34.4 years old for fathers.
And God blessed them, and God said unto them, Be fruitful, and multiply, and replenish the earth, and subdue it: and have dominion over the fish of the sea, and over the fowl of the air, and over every living thing that moveth upon the earth.
Genesis Chapter 1 Verse 28 of the King James Version of the Bible
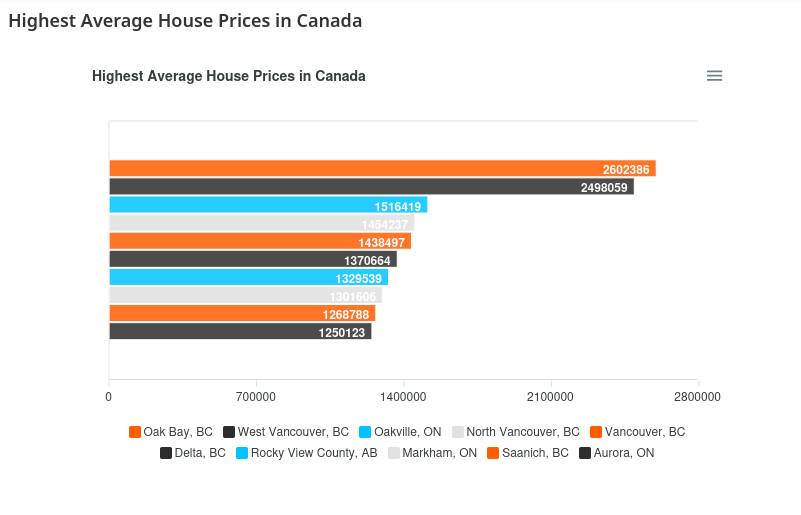
One of the main factors has been the economic uncertainty, especially with inflation tightening people’s budgets and making couples think that it’s not a good time to have kids. Canada’s biggest cities saw even lower fertility rates than the rest of the country. British Columbia had the lowest fertility rate of all Canadian provinces and territories, with only 1.11 children born per woman, likely due to the sky-high cost of buying a house in Vancouver, where most people in BC live. Here are some cheap places in Canada where you can buy a house.
Before learning about all this stuff about fertility let’s check out what the terms fertility rate and birth rate mean.
What is a Fertility Rate? What is a Birth Rate?
The total fertility rate (TFR) counts how many kids a woman is expected to have over her reproductive life if she experienced, at each age, the fertility rates observed over the course of a given calendar year. A similar metric is the birth rate, which counts the number of live births per 1000 individuals in a population over a given year. Let’s check out what has happened as a result of Canada’s record-low fertility rates.
Consequences of Record Low Fertility Rates
While Canada recorded its lowest fertility rates ever it also recorded its record for population growth in 2022. This was done almost entirely through immigration and temporary residents according to Statistics Canada. In 2022, Canada brought in a historically high number of 437,180 immigrants and saw a net increase of the number of non-permanent residents estimated at 607,782. Both of these numbers represent the highest levels on record.
Fertility Rates for the United States
The United States saw a fertility rate of 1.7 in 2021. The age of first-time mothers affected the fertility rate, with American mothers now being a historic average age of 27.3 years old when their first surviving child is born.
How do fertility rates vary by US state?
American states in 2021 varied in terms of birth rate. In 2021 the American states of North and South Dakota saw the highest birth rates. North Dakota‘s birth rate was the second-highest nation wide in 2021, with a birth rate of 66.7 births per 1000. North Dakota, along with Louisiana, was one of only two states that had an increase in birth rates between 2005 and 2021. North Dakota’s fertility rate increase of 2.93% between 2005 and 2021 was the greatest increase of any state in the United States.
North Dakota was a stand-out American state in terms of fertility in 2022. It ranked third out of all 50 states for the highest birth rate, only behind Utah and Alaska. State Data Center Demographer Kevin Iverson attributed this to the growth of North Dakota’s fracking industry in the Bakken Formation. This combined with a lower cost of living has attracted more young people that can have kids. Let’s pivot from North Dakota and see what’s causing South Korea to have so few kids.
South Korea’s Record Low Fertility
South Korea is the birth place of Samsung and many elite e-sports players. Despite that, it has the world’s lowest fertility rate of any country in 2021, with mothers only having 0.8 children on average. Some of the common reasons are:
- high childcare costs
- expensive housing that delays baby making
- economic uncertainty faced by young South Koreans after the Asian financial crisis of 1997 that lead to more unstable work
- a declining marriage rate
In 2018, South Korea also had the lowest fertility rate on the planet, with 1.1 children expected to be had for each woman. Singapore was right behind them. Let’s see how the Heng family managed to support a family of seven kids in the second least fertile country on the planet in 2018.
Raising 7 Kids in Singapore
In 2018 families in Singapore with one child were normal, where the fertility rate is 1.2 children expected by each woman. The Heng family went above and beyond by having seven kids in their family. In Singapore of all places, where in 2018 it was ranked eight most expensive country on the planet to live in. The Heng family managed to raise their family despite the financial, logistical and parenting challenges. Check out how they pull it off.
We’ve now seen how big families get it done in countries with low fertility. Let’s turn back to the US and Canada. Fertility hasn’t always been low in North America, so let’s rewind the clock and check out how the United States and Canada handled fertility over the course of over 200 years.
The History of American and Canadian Fertility Rate
United States’ Fertility Rate Throughout Time
In 1800 the typical American mother had an average of seven kids in her lifetime. Women usually had their first child at the age of 23 years old. They would have kids roughly two years apart until reaching her early 40s. A number that has since slowly dropped. In the late 18th century Benjamin Franklin attributed high fertility to
- easy access to good farm land
- no tithes in the states and barely any taxes
- political institutions were favourable to alienation and division of property
- cheap good land that supplies greatest quantity of healthy work affords the most valuable produce of society
Canada’s Previously High Fertility Rate
Canada, like the US, had a high fertility rate until the mid-1800s before a decline began. Until the early 20th century most people lived in rural areas, making it easy for couples to have big families. Kids helped grow their family’s wealth. They did this by sharing daily chores inside the house and out on the farm. Religion was very influential on families and there was no contraceptives being used.
Nearly a century passed and World War II had ended. The Canadian economy was strong between 1946 to 1965. Everyone got married and had a bunch of kids, with the baby boom period seeing its peak fertility rate in 1959 where the average Canadian woman had 3.94 kids in her lifetime.
The late 1960s is when things changed. Religion’s influence on daily life had faded away and contraceptives were more effective and available than ever before, such as the hormonal birth control pill. The hormonal birth control pill was no longer illegal in 1960. It was first allowed to regulate menstrual cycles and then used as a contraception in 1969, when “the pill” and therapeutic abortion were no longer illegal with Bill C-150. At the same time, women became more educated and started working more. This was a result of social changes, including the feminist movement, technological developments, and labour market shortages. In addition, changes to family law and divorce law in 1968 and again in 1986 made it easier for couples to get a divorce. More divorces happened as a result, affecting the number and timing of births for couples. As a result the Canadian fertility rate dropped.
While the pill changed the fertility game in Canada and many other countries, there are other things that affect a country’s fertility rates.
What Affects the Fertility Rate
The main factors that affect a country’s fertility rate are:
- the age of first-time mother
- use of contraceptives
- duration between a mother’s births
- education for women and girls
- government policies
Age of First-Time Mothers
The age of first-time mothers is the number one factor. Women that marry and have children earlier in life tend to have more kids in their lifetime. This is also because a younger mother has more eggs available to make kids with. A young age for first-time mothers usually is linked to mothers marrying earlier in life.
Women are born with all the eggs they will ever have. Each day the number of eggs drops daily from birth onwards. Only a few eggs are lost each day in young women. In ages 35-40 many eggs are lost daily and the quality of eggs drops too. This makes it harder to get pregnant. If there is a pregnancy during the ages of 35 or above there is a higher chance for a miscarriage to happen. Fertility in men also drops as they age, but to a lesser degree.
Duration Between a Mother’s Births
The duration between births measures how much time a mother waits between having multiple kids. For example, you may know older people that have five siblings with roughly three year age gaps or younger people with only one sibling that are seven years apart.
How Education Affects the Fertility Rate
The more educated women are the less kids a country has. This can be measured by looking at a country’s tertiary education completion levels. Canada is the most educated country on the planet, which recorded the lowest fertility rate in its history in 2022. Education, along with focusing on career and work, has become more important than a family and children to potential mothers that are still fertile.
Cost of Living
When life is expensive people don’t want kids, especially in developed countries. Right now a lot of us are dealing with stagnant wages, inflation driving the cost of living up, steep student debt in the form of tuition payments, houses that no one can afford, and some mean daycare costs. The economy, in many places, is not inspiring people. This makes people wait until they’re older and have their stuff together before they have kids. The countries with the lowest fertility rates are some of the most expensive countries on the planet. Currents example include South Korea, Singapore, Japan, Hong Kong, and Italy.
Government Incentives
The governments of Hungary, China, and Australia tried different ways to encourage people to have kids or to have less kids. In Hungarian government encouraged people to have kids by:
- a paid maternity leave until the child turns three years old
- family allowances to let employed or unemployed couples improve their homes, live in cheap public housing, or interest-free home loans
- giving €32,250 Euros to couples that have three or more kids
- free in-vitro fertilization (IVF) treatments
- tax allowances for mothers raising at least four kids
Next, the Australian government encouraged people to have kids by:
- allowing for flexible work hours, patterns, and locations for parents
- paid parental leave
- tax returns for daycare costs
- payments to single-income or single-parent families
And China, because of hammering out 6.3 kids per woman in 1968, decided to lower it’s fertility rate through its one-child policy between 1979 and 2015.
Family Planning & Contraceptives
Family planning, or contraceptives, are a way to encourage people to have less kids. Contraceptives are a birth control method to stop pregnancies from happening. There are things like condoms, abortions, hormonal birth control pills, intrauterine system devices (IUDs), injections, and many other methods. Let’s take a look at how contraceptives and family planning can be used on a global scale.
Bill Gates, Planned Parenthood, & Continuation of Family Traditions
On January 29th, 2010, Bill Gates pledged $10 billion to the World Health Organization (WHO) saying, “We must make this the decade of vaccines.” A month later Bill Gates had a TED Talk presentation in 2010 called “Innovating to zero!” focused on various issues including population. At around 4 minutes and 32 seconds of the video Gates said the following about population:
“The world today has 6.8 billion people. That’s headed up to nine billion. Now, if we do a really great job on new vaccines, healthcare, reproductive health services, we can lower than that by perhaps ten or fifteen percent.”
Bill Gates during his “Innovating to zero!” TED Talk on February 20th, 2010
This is not a new concept for the Gates family. His father Bill Gates Sr. worked on the boards of countless organizations including United Way, and serving as the head of Planned Parenthood, as stated by his son Bill Gates. Planned Parenthood was founded by Margaret Sanger, with the help of her sister, on October 16, 1916. It was the first birth control clinic in the US that worked as a sexual and reproductive healthcare center. She believed in eugenics, which labeled certain people unfit to have children and the idea that society can be improved through planned breeding for “desirable traits”.
Let’s keep in mind that there may be some fact-checking websites that have received funds from the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, such as PolitiFact. They received a donation of $70,000 in 2015 and another donation of $126,650 in 2016 from the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation to fact-check claims about global health and development in partnership with Africa Check.
Based on what’s happened in the past we can get an idea of how that Bill Gates can achieve a reduction of the world population by 10 to 15%. Let’s check out what happened in vaccine trials throughout the world.
The Kenyan Birth-Control Vaccine
In 2014, Kenya’s Catholic Doctors Association accused the WHO of chemically sterilizing millions of unwilling Kenyan women with a tetanus vaccine. Independent labs found a sterility formula in every vaccine tested. Similar accusations came from Tanzania, Nicaragua, Mexico, and the Philippines.
HPV Vaccine in Andhra Pradesh and Gujarat, India
HPV vaccination was introduced in India in 2008. In 2009 the non-profit organization Program for Appropriate Technology in Health (PATH) carried out a vaccine delivery and demonstration project in Andhra Pradesh and Gujarat. It was reportedly funded by a grant from Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation. This vaccination was given to 16,000 girls aged 9-15 years old. In 2010 it was suspended because of a public concern about its serious adverse affects (SAE) such as anaphylaxis, cardiac arrest, and seizures.
Many of the signed forms in Andhra Pradesh and Gujarat were mostly signed by illiterate parents or guardians who could not sign in their local language, such as Telugu or Gujarati. In Andhra Pradesh 9,543 forms were signed, 1,948 had thumb impressions while hostel warden had signed 2,763 forms. In the Gujarat 6,217 forms were signed, 3,944 had thumb impressions and 545 were either signed or carried thumb impression of guardians.
Before the trials started, the side effects were known including anaphylaxis (severe allergic reaction), syncope, convulsions, asthma, central demyelinating diseases, acute disseminated encephalomyelitis, and Idiopathic Thrombopenia Purpura. Despite this, PATH did not provide for urgent expert medical attention in case of serious adverse events. Manufacturer side effects were revised several times and now included serious health issues.
Consequently action on investigations into the causes of deaths took an unacceptably long time. A number of discrepancies and gaps in the investigations of the deaths have also been pointed out. There was no diary card-based reporting or recording of adverse events in the study protocol. This resulted in gross under reporting of the adverse events.
HPV Vaccine in Carmen de Bolivar, Colombia
In 2013, Colombia’s HPV vaccination rate was one of the highest in the world. The uptake rate of the HPV vaccine dropped from 96.7% after its introduction in 2013 to 9% in 2020. This is likely because of the Carmen de Bolivar event of 2014 happened, where a group of young women that were given the HPV vaccine in experienced fainting spells, weakness, limb paresthesia, chest pain, tachycardia, and headaches. The purported vaccine side effects were videoed by various media outlets and shared widely on social networks. Similar to the HPV vaccine trials in India things went sideways in Colombia because of:
- low knowledge of the vaccine by Colombian women before its introduction
- no articulation to the sexual and reproductive health policy
- lack of prior training of health workers at all levels of care
- non-specific communication plans for HPV vaccine
DTP Vaccines
Before 2017 neither the Health & Human Services (HHS) or World Health Organization (WHO) ever studied whether or not the DTP vaccine gave good outcomes by looking at people that did and didn’t get the DTP vaccine. In western countries, such as the United States, the DTP vaccine was no longer given because thousands reported death or brain damage. Bill Gates, GAVI, and the WHO, started prioritizing African babies.
The Danish government & the Novo Nordisk Foundation commissioned this study, featuring a team of the world’s top experts on African vaccination. The two most prominent names, Drs. Soren Mogensen and Peter Aaby were vocal vaccine supporters. They saw the results of the “natural experiment” in Guinea Bissau, showing that 50% of children that got the DTP vaccine died before age 5. Half of those kids got the DTP vaccine at 3 months old, and the other half got it at six months old. The study found that kids that got the DTP vaccine died five times more than kids that didn’t get it. While kids with the DTP vaccine protected themselves from Diphtheria, Tetanus and Pertussis, they exposed themselves to other deadly diseases. This compromised their immune systems. Gates made DTP arguably the most popular vaccine in 2020.
Malaria Vaccine in Seven African Countries
In 2010, the Gates Foundation funded a phase 3 trial of GSK’s experimental malaria vaccine, killing 151 African infants and causing serious adverse effects including paralysis, seizure, and febrile convulsions to 1,048 of the 5,949 children.
The Oral Polio Vaccine in the Democratic Republic of Congo
In 2018 the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) saw polio spread like fire and paralyzed 29 children. This is because a rare mutation from the weakened live virus in the oral polio vaccine (OPV) regained its ability to cause disease and also its ability to spread. The circulation of vaccine-derived polioviruses (cVDPVs) appears to be the greatest threat to polio eradication.
Along with the 2010s being dubbed the decade of vaccines, digital IDs or certificates, are of high interest to Bill Gates. Let’s see what that’s all about.
Digital IDs or Certificates
On March 18th, 2020, under the username thisisbillgates, Bill Gates hosted a AMA (Ask Me Anything) on Reddit about COVID-19 panic that was going on. In that AMA a user named RemoteControlledUser asked the following question:
What changes are we going to have to make to how businesses operate to maintain our economy while providing social distancing?
RemoteConrolledUser, a Reddit user asking during Bill Gates’ Reddit AMA about the onset of COVID-19
Gates answered with:
The question of which businesses should keep going is tricky. Certainly food supply and the health system. We still need water, electricity and the internet. Supply chains for critical things need to be maintained. Countries are still figuring out what to keep running.
Eventually we will have some digital certificates to show who has recovered or been tested recently or when we have a vaccine who has received it.
Bill Gates, aliased as thisisbillgates, during his Reddit AMA about the onset of COVID-19
How ID2020 Can Deliver Digital IDs & Certificates
In 2019 a company name ID2020 Alliance launched a new digital identity program at its annual summit in New York in collaboration with the Government of Bangladesh and GAVI. They defined digital identity as a computerized record of who someone is that is stored in a registry. It can track someone’s proof of vaccination, refugees, and people without IDs. In ID2020’s article on Medium they presented the following benefits to a digital ID:
- they can improve coverage rates & vaccine compliance
- perform immunization in infancy
- give children a digital child health card
- give children a unique portable digital identity early in life
- grant access to a wider range of social services
Revelation Chapter 13 verses 16 to 17 of the King James Version of the Bible
16 And he causeth all, both small and great, rich and poor, free and bond, to receive a mark in their right hand, or in their foreheads:
17 And that no man might buy or sell, save he that had the mark, or the name of the beast, or the number of his name.
Digital IDs Being Rolled Out to Bangladesh
In August 2019 ID2020 partnered with the Ministry of ICT of the Government of Bangladesh, and GAVI, the Vaccine Alliance to solicit responses for a Request for Information (RFI). A2i and its partners GAVI and ID2020 teamed up to research and roll out their digital ID in Bangladesh through vaccination.
The True Source of Good Health
Global public health advocates around the world accuse Gates of steering the WHO away from the projects that are proven to curb infectious diseases: clean water, hygiene, nutrition, and economic development. The Gates Foundation only spends about $775 million of its $7 billion dollar budget on these areas.
Bonus: A Chemical Found in Cheerios Cereal & Quaker Oats That Could Adversely Affect Fertility
Around 80% of Americans have been exposed to the plant pesticide chlormequat, which causes fertility and growth issues in animals. This chemical is found in many oat-based foods, such as Cheerios and Quaker Oats. Rats that were exposed to it had lower sperm motility, lower male testosterone levels, delayed puberty, and lowered weights of male reproductive organs, according to the study. Concentrations of chlormequat in the urine samples of Americans rose from 69% in 2017 to 90% in 2023. Other studies found it caused no affect on fertility and the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) said there were no adverse reproductive risks in humans, female mice or male pigs, male mice.
Summary
It seems like the countries with the lowest fertility rates live in have mothers that marry and give birth later in life, have long gaps of time between each child that is born, are highly educated and focused on work, use contraceptives and family planning, and have a high cost of living or an economy that discourages people from having kids.
Canada’s reached a record-low fertility rate. It could be by design or something out of control. What do you think has caused Canada’s fertility rate to drop so low? Is it the economy dunking on everyone? Is it because of how hard it is to move out from mom or dad’s place? Leave your answers in the comments below and be sure to share the content!


